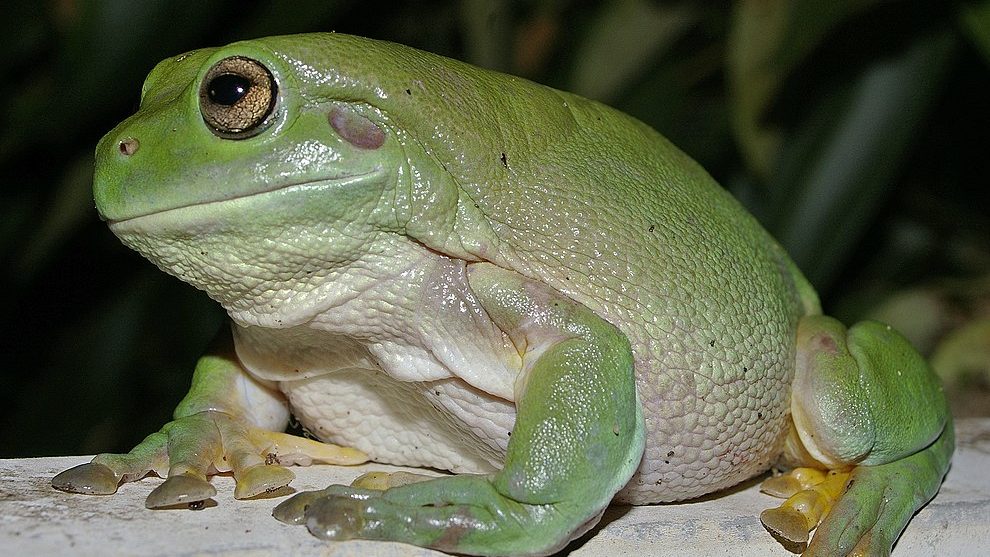
Why Do Whites Tree Frogs (otherwise known as Australian Green Treefrog) change color and How Do They Do It? The following article will answer these questions: Do Tree Frogs All Change Color? Do Whites Tree Frogs Change Color, and What Kinds of Tree Frogs Change Color? Read on to learn more.

Do All Tree Frogs Change Color?
Why do tree frogs change color? Tree frogs change color to attract a mate. There are several reasons for this. The frogs may have seen a predator, been frightened by a spooky noise, or may be searching for food.
Other reasons include temperature and movement. Here are some common reasons for the change in color of white tree frogs.
Some White tree frogs change color to brown when they’re stressed or sick. If you notice any of these signs, you should take your frog to the vet. The vet will be able to examine your frog and decide whether it needs medical care.
Then you can decide whether or not you should take it to the vet for proper treatment. Generally, white tree frogs can live for up to 16 years, but they are much shorter in the wild.
Why Do Whites Tree Frogs Change Color?
Most species of Tree Frogs change color at least once during their life cycle. This process may take several days or months and is called morphological. It involves the morphing of pigment-containing cells in the outer layer of the skin, called Chromatophore.
The result is a different color. During one mating season, this change is temporary. In other seasons, however, it is permanent.
In captivity, a Whites tree frog changes color from white to dark brown. Humidity increases, and their substrate becomes wet. The presence of an overly wet substrate promotes the growth of mold and fungi, which can be deadly for amphibians.
This change in color may lead to decreased life expectancy. Life expectancy in the wild is significantly lower, but the species may reach 20 years in captivity.
How Do They Change Color?
Physiological changes in frogs are a natural part of the animal kingdom. Tree frogs change color for various reasons, such as to attract a mate. Their colors change due to environmental factors, including light intensity, the environment, and stress. Here is a brief explanation. The morphological change occurs at the time of the first mating season, and the colored phase is permanent.
The color changes of Tree Frogs are a natural defense against predators and other animals and may also be a means of communication. This is why they often change colour in response to physical disturbance or threat.
They may also be able to change their colours based on the temperature in their environment. The reason for this adaptation is not entirely understood, but there are several theories.

Monochromatic vs Dichromatic Frogs
There are two main types of frogs: monochromatic and dichromatic. Monochromatic frogs are typically green, while dichromatic frogs can be any color. Both types of frogs have pros and cons.
Monochromatic frogs are harder to spot in their natural habitat, which can be an advantage if you’re trying to avoid predators. They’re also less likely to stand out in a crowd, so they’re less likely to be picked off by predators that are looking for easy prey.
However, monochromatic frogs can also be more difficult to find when you’re looking for them, and they can be harder to photograph since they don’t have as much color.
On the other hand, Dichromatic frogs are easier to spot and photograph since they have more color. This can be an advantage if you’re trying to find a specific frog or if you want to take pictures of frogs in their natural habitat. However, dichromatic frogs may be more likely to stand out in a crowd and be picked off by predators since they’re more visible.
Conclusion
The cause of this unique morphological adaptation is not completely understood, but the process of chromophores is related to hormonal changes. The frog’s color is dependent on different factors, such as the amount of light and background color.
A physical disturbance triggers the changes to the frog, which in turn triggers a hormone response to prevent predators from preying on the frog.
In the study, we found associations between different blood parameters and skin color. We also found a relationship between plasmatic protein and coloration. However, we cannot be sure that color is directly related to body condition.
Moreover, the levels of protein and glucose were positively related. These findings suggest that the frogs’ body condition is related to their skin color, not vice versa. In addition, the study found differences among different populations of the same species.