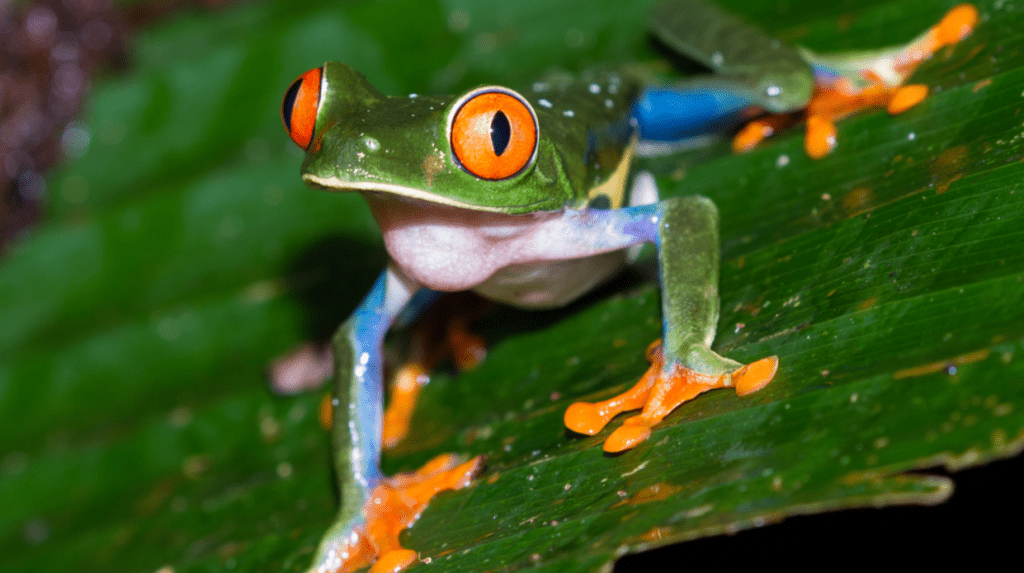
Do frogs have ears? This is a common question, and one that’s easy to answer. Frogs do have ears, but they are very different from human ears. The outer ear of a frog is called an auditory capsule. When you look at the outside of a frog, it looks as if there’s nothing there. But inside the frog, there’s an entire system designed to let the frog hear what’s going on around it.
The outer ear allows us to hear sound and provides balance; the inner ear enables us to hear sounds in detail and understand their meaning. What Do Frog Ears Look Like? Frogs don’t have external ears like humans or other animals with well-developed hearing. Instead, they have a pair of openings called tympana located in the front part of their heads called “snout.”
Some amphibians such as treefrogs can also make a chirping noise by rubbing substances against their vocal sac and vocal cords which makes them similar to birds in this regard.
How Do Frogs Hear?
Frogs have a unique way of hearing. They are able to hear the frequencies in the air and use this information to help them hunt for food, avoid predators, and communicate. Even though frogs don’t have external ears, they have an advanced inner ear system with a complex network of cells that enable them to hear sounds just like humans do. Frogs can also produce chirping noises when they rub their vocal sac and vocal cords together which is similar to the sound produced by birds.

How to Identify Frog Ears
The best way to identify frog ears is by looking at the bottom of their feet. When a frog is standing on land, its set of toes have pads that look like little “ears.” This is because these pads are under the webbing between the toes and are covered with cells that can vibrate rapidly to help a frog detect nearby sounds.
Do frogs have ears?
Yes, frogs do have ears, but they are very different from human ears.
What Do Frog Ears Do?
The outer ear of a frog is designed to send sound signals to the inner ear. These signals are used to determine not only how much sound is entering the inner ear, but also the direction and distance of the sound.
Other Uses of Frog Ears
Frogs also have a pair of eyes, which is less common among amphibians. The eyes of frogs are very different from human eyes as well. For example, frogs cannot see in color like humans do, but they can detect light and dark. One of the biggest differences between human and frog vision is that amphibians can sense vibrations coming from the ground, water or air. This allows them to move at high speeds without getting exhausted.
Are Frog’s Ears Useful to Them?
Frogs don’t have ears like humans, but they do have an auditory system that allows them to hear and interpret noises. This is a highly complex system made up of numerous little tubes, some of which are sensitive to low-frequency vibrations. These sounds travel through the body of the frog from its legs, into its head, and then into its auditory capsules. The sound waves cause a physical response in the ear called “cochlear feedback,” which makes it difficult for frogs to hear anything quieter than about 30 decibels. For comparison, people can hear sounds in noise as low as 10 decibels.

The Bottom Line
A frog’s ears are much different from human ears, but they can hear and distinguish sounds very well.